in each reaction box, place the best reagent and conditions from the list below
How To Solve “Place The Best Reagent In Each Reaction Box” Problems
Reaction Box problems are quite difficult to solve. Here are some tips that might help you.
Step 1: Analysing the reaction
In this process, you’re supposed to observe the given reaction.
You can easily tell compounds are:
- Saturated or unsaturated
- Aliphatic or aromatic
Step 2: Count the number of carbons on both sides
The carbon number has to be reduced by one to find out if carbon numbers are decreased or increased.
Step 3: Figure out the IUPAC name of given compounds
It is better to write correctly the IUPAC name of both compounds and understand their behavior and type of reaction applied.
Step 4: Choose the best reagent and conditions
The most difficult steps are choosing the best reagent and conditions for this problem.
It’s important to understand the steps to take to achieve your Amazon business goals.
Simply by focusing on the given reagents and conditions, and figuring out what they are.
- Oxidizing and reducing agents
- Acidic and basic reagents ( If a molecule has more than one acidic proton then we should know which one will be abstracted first )
Step 5: Know basic named reactions types
To convert an organic compound into its other form you need to know about the various types of reactions and the compounds involved in the reaction.
Here are some of the most common named reactions that people use, such as:
- Halogenation (Eg. Hoffmann Bromination)
- Oxidation and reduction
- Nitration
- Hydrolysis
- Carboxylation and Alkyl Cyanide formation ( It can be used if you want to increase carbon numbers.)
- Hunsdiecker reaction and iodoform preparation (used if you want to reduce carbon numbers)
These are some additional famous reaction types methods:
- Markovnikov and Anti-Markovnikov methods
- Heinsberg’s method
- Ozonolysis
- Grignard’s method
- Functional group rearrangements
Based on the above five steps, we have some different types of reactions for the problem “In Each Reaction Box, Place The Best Reagent And Conditions From The List Below” which will definitely clear all your doubts and you will be master in such problems.
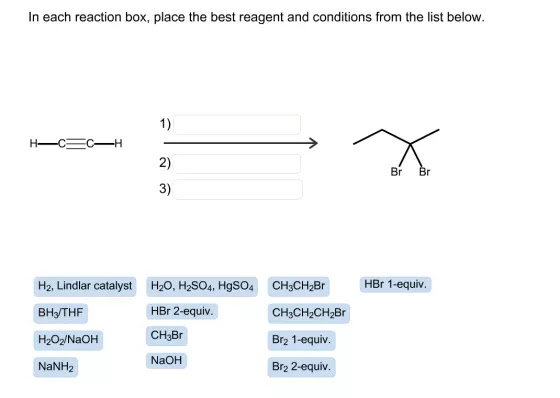
Example 1: (Three boxes total)
Answer:
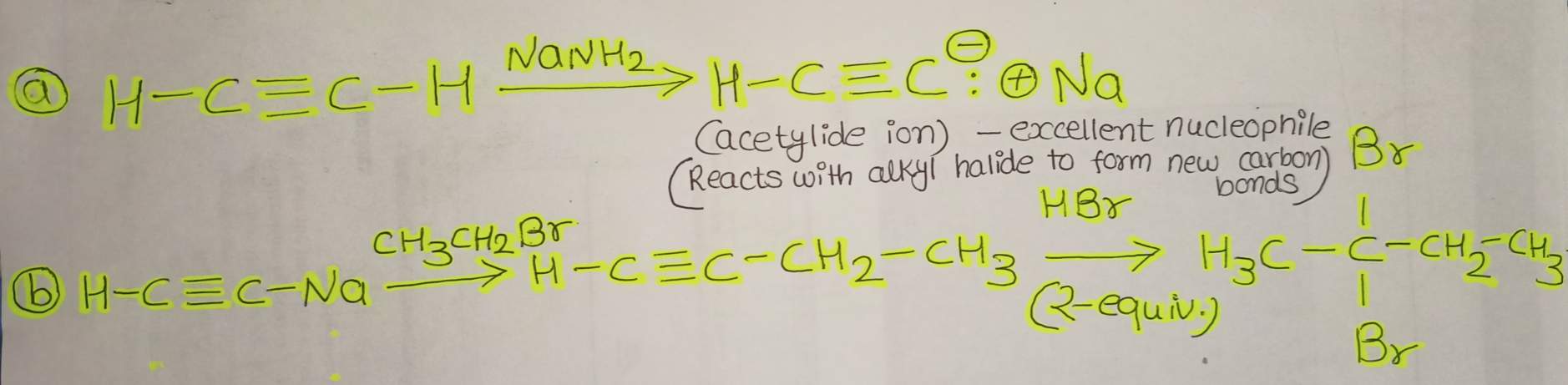
Step-by-step explanation:
- On the left side, the given structure has two carbon atoms connected by a triple bond and another double bond to a carbon with a triple bond. And on the right side, the structure has four carbon atoms connected by a single bond and two bromine atoms attached with the same carbon atom which IUPAC name is 2,2-dibromobutane.
- Here the number of carbons is increased and the triple bond is also changed into single bonds. Acetylide ion is one of the best nucleophiles, so you first need to use sodium amide.This is because it can easily react with alkyl halides to form a new carbon bond.
- Our final product has four carbons, so we have to add two more carbons, which is CH3-CH2-Br. Butyne is an intermediate molecule in the formation of propene, which contains one carbon and four hydrogen atoms.
- The reaction we had in mind was to add two bromine groups and reduce triple bonds into single bonds. For that, we should add two equivalents of HBr (i.e.Br2-Equiv.). When this reaction occurs, the first one bromine reduces triple bond to double bond and the second bromine reduces double bond to a single bond. Here is our final product successfully!
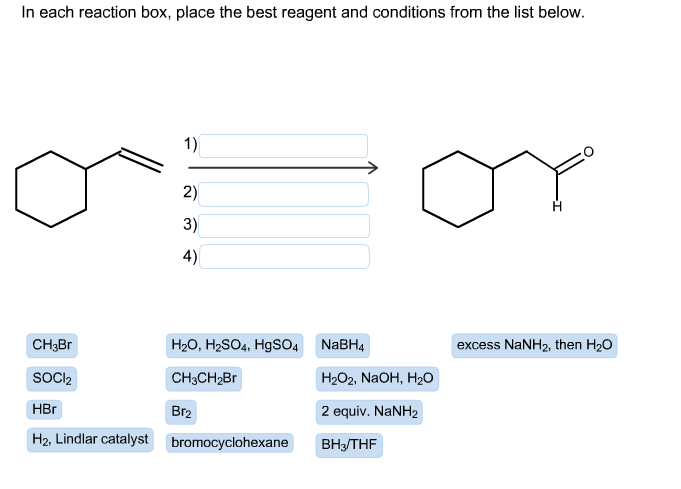
Example 2: (Four boxes total)
Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
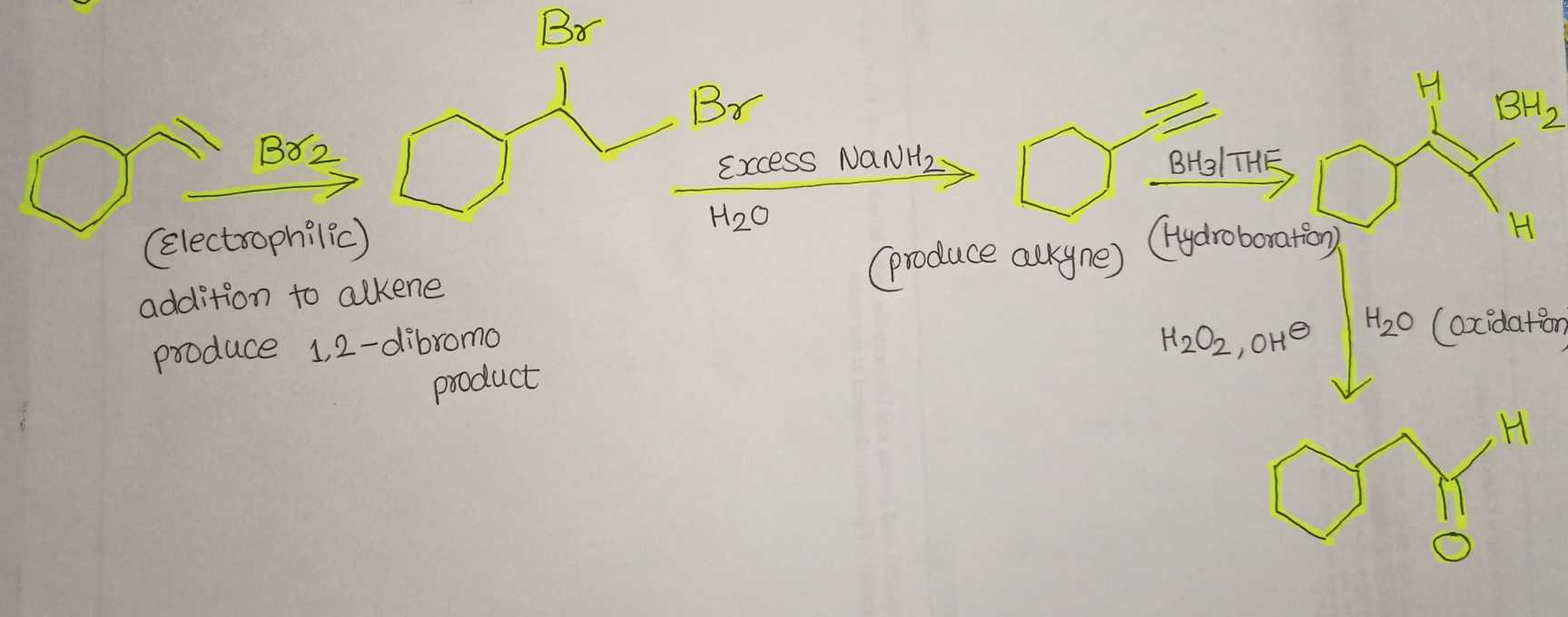
- In this given conversion reaction, an aromatic compound that is attached with an alkene ended with an additional -OH functional group at the end. These are our general analysis.
- Our analysis suggests that we need to use a strong electrophile to get 1,2-dibromo product.
- By using excess NaNH2 and then H2O, we can produce alkynes.
- Now that we have a look at the formation of an alkynyl group, it’s time for the hydroboration.
- The -OH functional group was added to our molecule by adding H2O2 and sodium hydroxide.
